Understanding TFT LCD Display Interface Pin Definitions
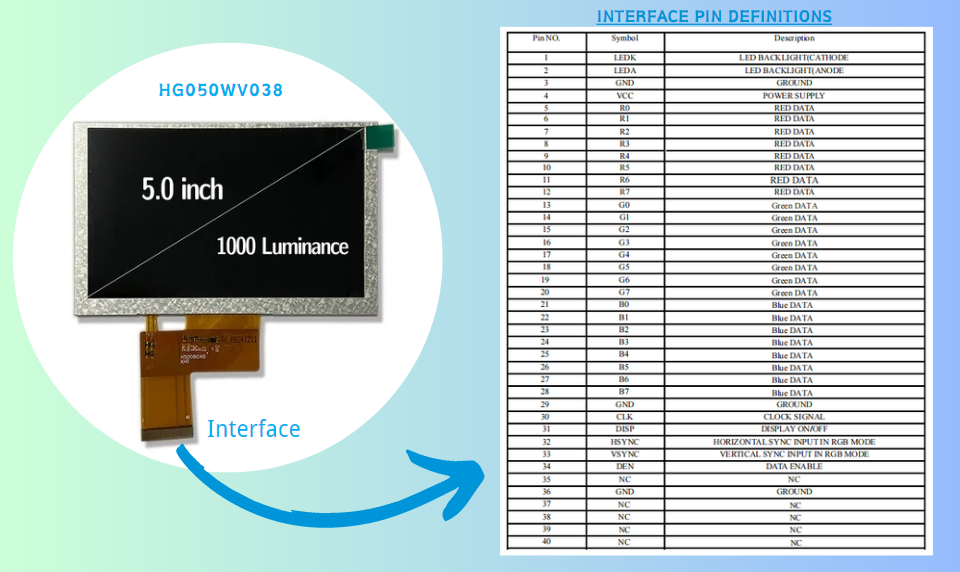
TFT LCD display are widely used in various electronic devices, and understanding their interface pin definitions is essential for integrating these displays into projects.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the common pin definitions found in TFT LCD interfaces, focusing on key aspects such as functionality, types of interfaces, and practical applications.
Common interface types
TFT LCD displays can utilize different types of interfaces, each with its own set of pin definitions.
Here are some of the most common interfaces used in TFT LCDs technology:
RGB (Red, Green, Blue)
RGB interface is a parallel interface that transmits color data for each pixel using separate pins for red, green, and blue components.
This method typically requires multiple pins, usually arranged in a 24-bit configuration (8 bits per color). RGB interfaces are straightforward and commonly used for monitors and televisions.
They provide high-quality color reproduction, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface)
MIPI interface is a high-speed serial interface designed primarily for mobile devices.
It enables efficient data transmission with low power consumption, making it ideal for smartphones and tablets.
MIPI DSI (Display Serial Interface) specifically handles video data, providing a compact solution that can support high resolutions and refresh rates.
Its differential signaling helps reduce electromagnetic interference, enhancing performance.
eDP (Embedded DisplayPort)
eDP inerface is another high-speed interface commonly used in laptops and desktop monitors.
It supports higher resolutions and refresh rates, making it suitable for modern displays. eDP also features power management capabilities, allowing for reduced power consumption during operation.
This interface is advantageous for applications requiring high-quality graphics and video output.
LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling)
LVDS interface a widely used interface that transmits data using differential signaling, which helps minimize noise and improve signal integrity.
It is commonly found in high-resolution displays, such as televisions and computer monitors.
LVDS can transmit multiple channels of data simultaneously, allowing for higher bandwidth and better performance.
This makes it a popular choice for applications requiring fast data transfer rates.
Typical pin definitions
Here are some common pin definitions found in TFT LCD display interfaces:
Power pins
VCC (Power Supply): This pin provides the positive voltage necessary for the display operation, typically ranging from 3.3V to 5V.
GND (Ground): The ground pin connects to the system ground to complete the electrical circuit.
Data pins
Data Pins (D0-Dn): For parallel interfaces, these pins are used to transmit data. The number of data pins varies depending on the display (e.g., 8-bit or 16-bit). Each pin corresponds to a binary digit (bit) of the data being sent to the display.
Serial Data (SDI): In serial interfaces, this pin is used to transmit data one bit at a time.
Control pins
RS (Register Select): This pin determines whether the data being sent is command data or display data. A high signal often indicates data, while a low signal indicates a command.
R/W (Read/Write): This pin indicates the direction of data flow. A high signal typically means data will be read from the display, while a low signal indicates data will be written to the display.
E (Enable): This pin is used to latch the data into the display. A high-to-low transition on this pin will trigger the display to process the data present on the data pins.
Additional pins
BL (Backlight): This pin controls the backlight of the display. It may be connected to a power source or controlled via a PWM signal for brightness adjustment.
CS (Chip Select): In some interfaces, this pin enables or disables the display. When low, the display is active; when high, it is inactive.
Practical applications
Understanding TFT LCD pin definitions is crucial for various applications, including:
Embedded Systems: When designing microcontroller-based systems, knowing how to interface with TFT LCDs is essential for displaying information.
Consumer Electronics: TFT LCDs are prevalent in devices like smartphones, tablets, and televisions, where precise control over display functionality is required.
Industrial Equipment: In industrial settings, TFT LCDs are used for control panels and monitoring systems, necessitating reliable communication through well-defined pin interfaces.
Conclusion
Mastering the pin definitions of TFT LCD display interfaces is vital for engineers and developers working with these technologies.
By understanding the various power, data, and control pins, as well as the types of interfaces available, one can effectively integrate TFT LCDs into diverse applications.
Whether for consumer electronics or industrial systems, this knowledge is foundational for successful display implementation.
For further information on specific TFT LCD pin definitions, consulting the datasheet of the particular display model is always recommended.

